What is DFA?
DFA (Design for assembly) is defined as a process of designing such that it can be assembled easily and at a low cost. In DFA analysis is done on child parts and the final product for any assembly problem early in the design stage. It is important as it potentially reduces the assembly cost.
Purpose of DFA?
- To simplify the product so that the cost of assembly is reduced.
- To improve the quality and reliability of the product.
- It also reduces inventory costs and production equipment requirements.
Method of Assembly:
- Manual assembly: Capital cost is low. The cost per unit is also low.
- Fixed automatic assembly: In an injection molded process the number of units produced is greater and the unit cost is low.
- Robotic Assembly: Capital costs are higher. The cost per unit is very low.
| Manual Assembly | Fixed Automatic Assembly | Robotic Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Capital cost low | Nos of units produced more | Capital cost high |
| Unit cost low | Unit cost low | Unit cost low |
Design guidelines for manual assembly:
- Eliminate the need for operators to make decisions or settings. Ensure foolproof assembly so that there is only one way whether sequence or orientation.
- Ensure accessibility and visibility. Make everything self-aligning.
- Eliminate the need for assembly tools and gauges. Make parts self-locating and self-orienting.
- The number of parts should be minimal. The number of bolts and screws should be minimum.
- The number of different parts should be minimal. Bolt and screw should be of the same size.
- Avoid part orientation during assembly.
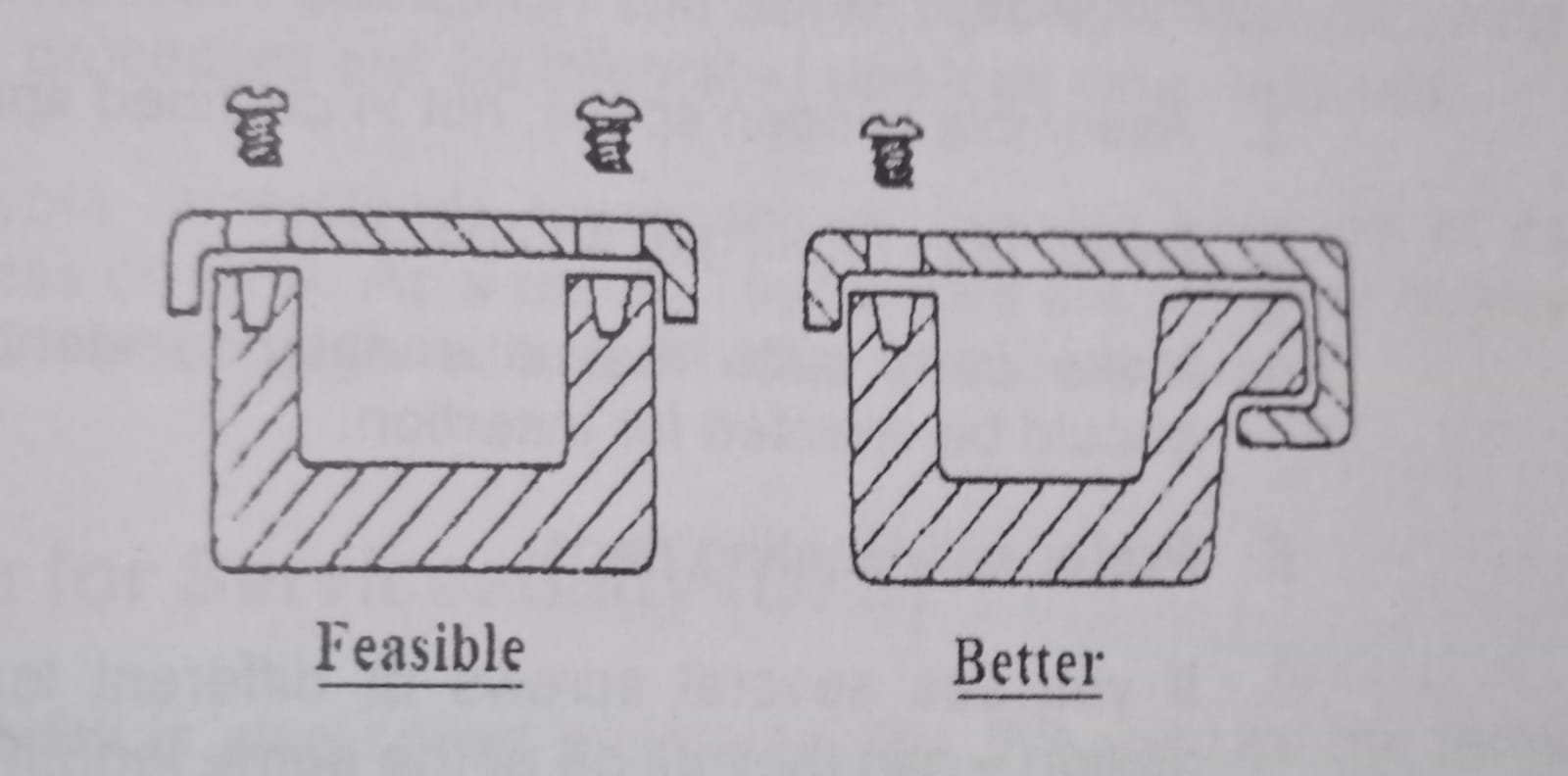
Design guidelines for automated assembly:
- Use self-aligning and self-locating features.
- Minimize bolts/screws. Avoid if possible.
- Use the largest and heaviest parts as the base of the assembly.
- Use standard parts and materials.
- Use parts that can be fed automatically.
- Design parts with a low center of gravity. It makes parts more stable during assembly.
- Reduce the number of different parts.
You may like to know about Design for Manufacturing
Problems if DFA not done:
- Every additional part is an opportunity for a defective part and assembly error.
- Increase the total cost of assembly.
- Make automation more difficult and more costly.
- Cost related to purchasing, and inventory increases.
Design for manufacturing (DFM) and design for assembly (DFA) should be done same time. Then it can be called design for manufacturing and assembly ( DFMA). Toyota understood the importance of Design for assembly and uses 15 – 20% less parts than other OEM.

