In the fast-paced automotive industry, small changes in Man, Machine, Material, or Method (4M) can have a big impact on product quality and customer satisfaction. Managing these changes systematically helps organizations reduce risks, improve traceability, and comply with standards like IATF 16949.
This article explains the purpose, scope, examples, tools, and benefits of 4M Change Management with simple, practical insights.
Purpose of 4M change:
To record 4M Changes (Operator change, machine change, tool change, material & method change) management for expected change (New operator, operator on leave, machine/tool PM, New machine, new gauge & new instrument) and unexpected changes (Tool breakage, power failure, machine breakdown etc.)
If any issues arise later at the customer end, we can easily track the change details through 4M change management.
Scope of 4M change:
Applicable for all internal changes in man, machine, material and method in process & bought-out parts (BOP)
Responsibility of 4M Change:
| S.No | Activity | Responsibility | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Change Point Control Board | Supervisor | Daily |
| 2 | Change Approval | Plant Head / Quality Head | Daily |
Definition of Change :
Change related to a product or process is defined as the ‘man, material, machine and method used for‘ and is not as per the control plan, work instruction, skill matrix and customer approval.
What is 4M Change Management?
4M Change Management is a structured approach to record, track, and control changes in four areas of manufacturing. It is the systematic approach to dealing with the changes in Man, Material, Machine and Method.
- Man (Operator): Who operates the machine
- Machine (Equipment & Tools): Which equipment or tool is used
- Material: What raw material or supplier is used
- Method: How the process or inspection is carried out
It helps in identifying root causes of issues, preventing defects, and ensuring stable production.
Why is 4M Change Important?
- Prevents quality issues caused by unapproved changes
- Provides traceability during audits or customer complaints
- Improves confidence of OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers
- Reduces rejection, rework, and warranty claims
Planned VS Unplanned Changes:
Plan Change (Expected Change):
Change that occurs with prior information to the concerned person and defined action is taken to control the occurrence of non-conformity of the product at the change point.
Example of Plan change :
- The machine under Plan Maintenance
- Tool under Plan Maintenance
- A new operator is employed on the machine
- An operator working after a long leave
- The operator left the workplace due to urgent work
- New instrument used
- New machine used
Learn about Machine Maintenance and Tool Maintenance. procedures.
Unplanned Change (Unexpected Change):
A change that occurs without prior information to the concerned person and a sudden defined action is required to control the non-conformity of the product at the change point.
Example of unplanned change :
- Machine under Breakdown
- Tool / Die under Breakdown
- Tool breakage
- Power Failure
- Different grade materials are used
- Unapproved material sources used, etc.
If any changes are made in Man, Machine, Material, or Method related to the process, the change shall be immediately updated on the 4M change monitoring board & recorded in the 4M Change Tracking Sheet.
- The respective team informs to 4M change responsible person about any kind of changes in man, material, method and machine that happen in his area.
- The change details of Man, Material, Method, and Machine will be highlighted on the 4’M change control board.
- Identify the man change as per the man-machine matrix.
- The 4’M change responsible person shall update the 4’M change tracking sheet within 30 minutes and take suitable action as per the 4’M Change Work Instruction.
- If no change is there, the 4’M change responsible person shall fill the 4’M tracking sheet with green color and if there is a change, he shall fill it with red color.
- In case of any change, information is to be given to the concerned departments and control action is to be taken as per the WI.
Benefits of 4M Change Management:
- Ensures quick problem tracing in case of defects or recalls. Easy to trace defects at the supplier end
- In the situation of recall at OEM, it also helps to detect defective products.
- It provides confidence to OEM and Tier 1 companies when it gets 4M change records timely manner from its supplier.
- Reduces rejection, rework, and customer complaints
- Builds trust with customers through transparent change records
- Strengthens compliance with IATF 16949 requirements
- Enhances operator and supervisor awareness of process stability
Examples of 4M Change:
Man (Operator) change examples:
- The operator is on leave with the information
- The operator is on leave without information (start of shift)
- New operator working on the machine (New Hire)
- The operator is on long leave ( More than 45 days)
- The operator leaves the workplace due to urgent work (Short Leave)
- The operator suddenly leaves the workplace due to an accident/injury
- The operator suddenly left the workplace due to illness
- Start a new shift
- New shift in charge/supervisor/team leader
- Job rotation
- Adding or replacing an operator to improve cycle time.
- Untrained, unfamiliar operator due to absenteeism, illness and injury.
In the above examples, points 1 to 4 are planned changes and points 5 to 6 are unplanned change. If we use the same skill level operator in all conditions, then it is OK & to do setup approval only. But if we have to use unskilled operators, then it becomes an abnormal situation. Then take containment action (100% visual inspection & 5 parts recording or as per WI) also on that day.
In case of new operators, provide training as per operation standards and take containment action for all production of that day. For unplanned changes, take a retroactive inspection of all parts from the last inspection.
Machine (Tool) change examples:
- The machine is under preventive maintenance.
- Machine under breakdown
- The new machine (equipment), Tool, Jig and Fixture installed
- Tool under preventive maintenance
- Tool under breakdown
- Introduction, modification or removal of Poka Yoke.
- Poka Yoke bypass
- Equipment location change (Layout change)
- Equipment parameter adjustment outside a defined range
Method change example:
- Process parameter change
- Layout change
- Process method change
- Inspection method change
- Packing method change
- Process Flow change(Temporary or Permanent)
- New work instruction, Inspection sheet, Operation standard
- Revision in work instruction, Inspection sheet, Operation standard
- Temporary switch from auto to manual
- Temporary change to operator tools
- Additional inspection due to a quality issue
Material change example:
- Material received from another approved source
- Material received from other unapproved sources
- Different grade materials are used
- Supplier location change
- A material change in design
Tools for Effective 4M Change
1. 4M Change Tracking Sheet
Captures details of changes, corrective actions, and results.
2. 4M Change Control Board
Displays updates within 30 minutes of a change for transparency.
3. Man-Machine Matrix (Skill Matrix)
Helps assign only trained operators to machines.
4. Retroactive Inspection
Checks parts produced before an unplanned change to ensure quality.
5. 4M Change Approval Report
Approval from the Quality Head, Plant Head, or Customer before restarting processes.
6. 4M Change Tag
Used to identify materials or processes under change for traceability.
WI for 4M Change:
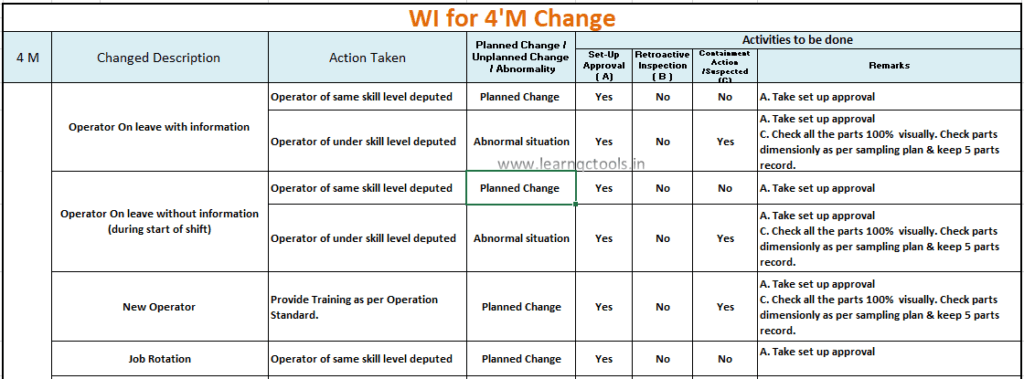
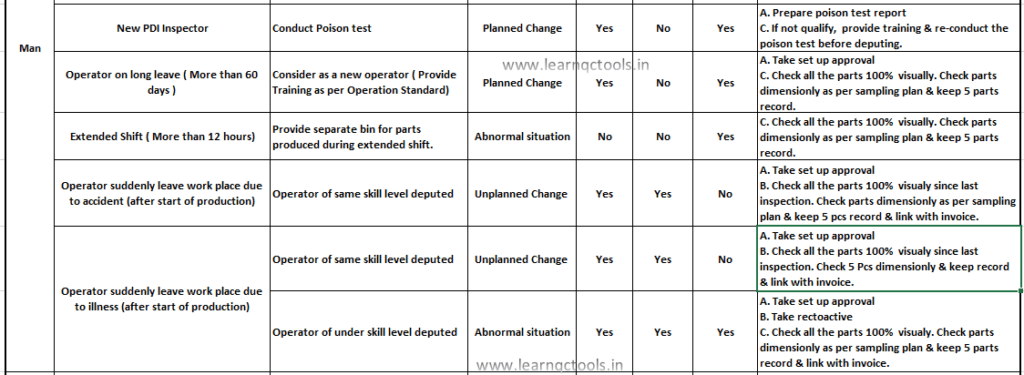
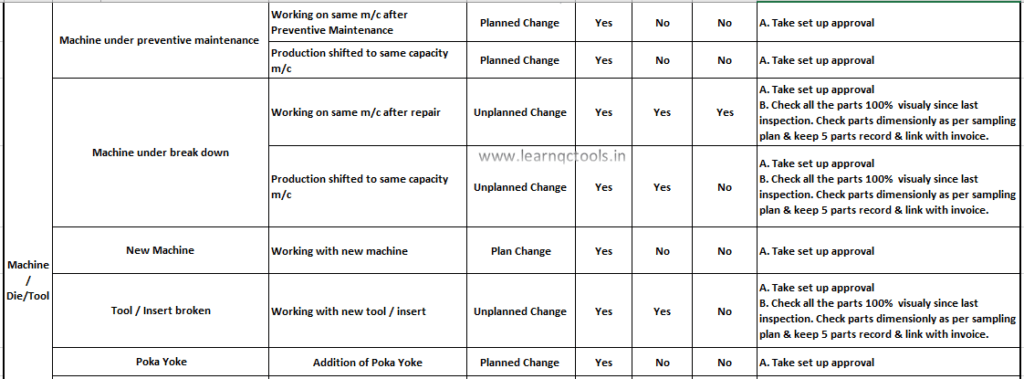
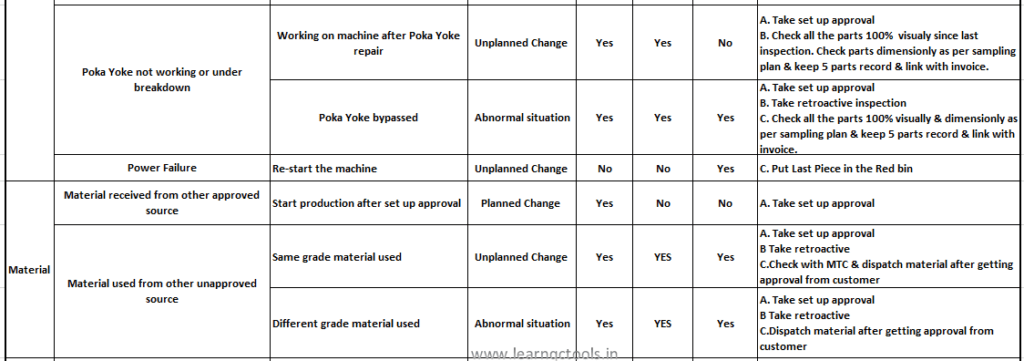
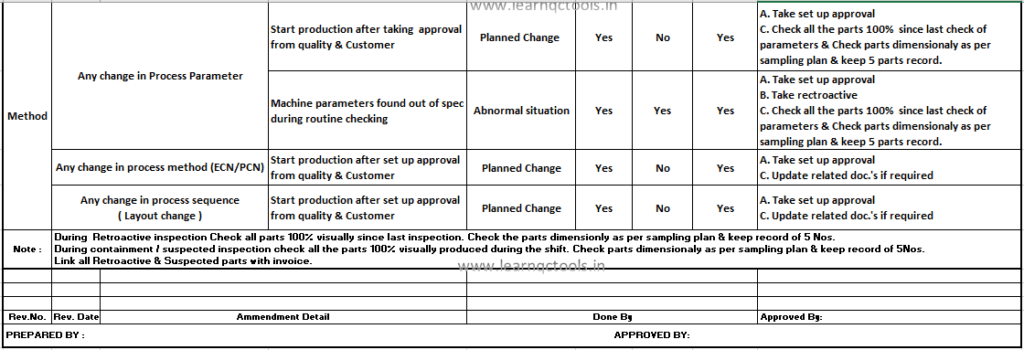
4M Change Tracking Sheet:
In the Tracking sheet, we prepare a summary of all the changes in the process & their detail. It contains the date of change starts, Type of change, changes in the description, what action was taken during the change, Machine or tool detail, Part name, Retroactive record, Containment record & dispatch detail etc. It is also called the 4M change record sheet.
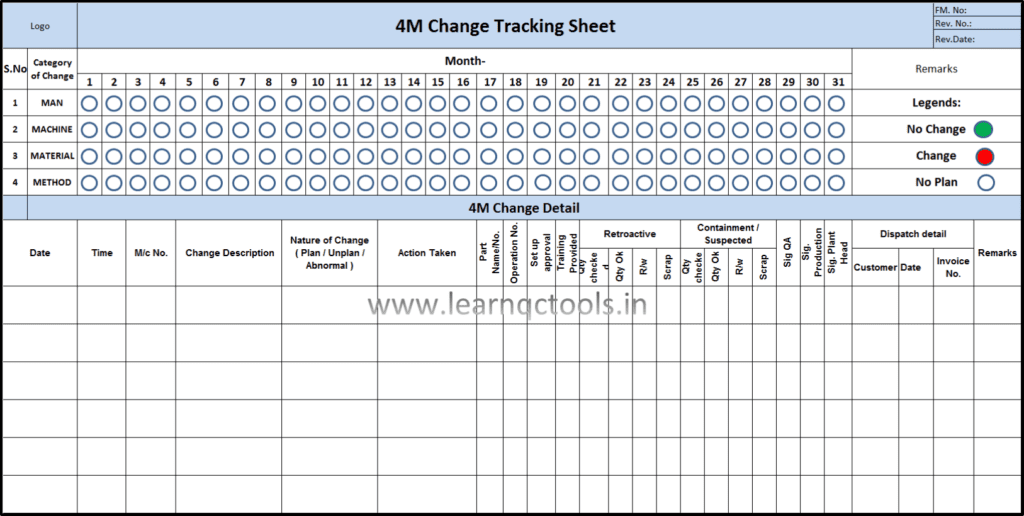
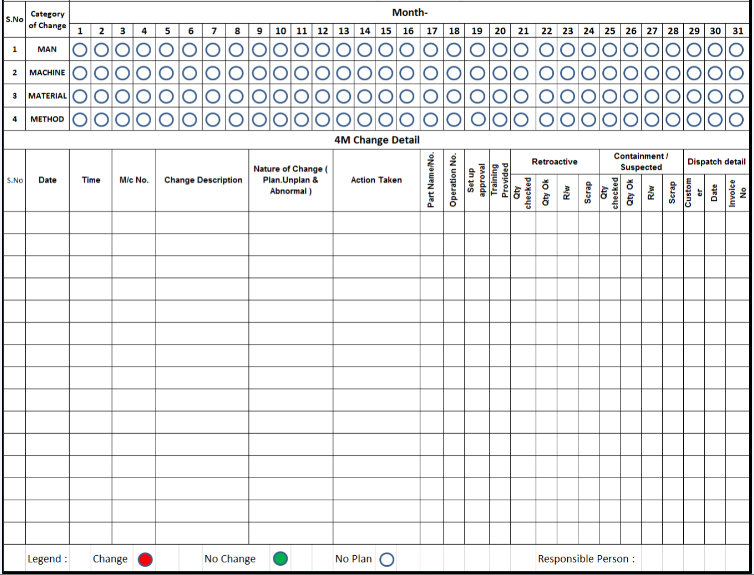
Download the sample 4M Change Tracking Sheet for your factory | 4M change format in Excel:
4M Change Control Board:
In the 4M change control board, we update all the changes in the process & their detail within 30 minutes of the change. It contains the date & time of the change starts, Type of change, changes in the description, what action was taken during the change, Machine or tool detail, Part name, Retroactive check record, Containment record & dispatch detail etc. The responsibility to update the 4M change board is of the production supervisor.

MAN-MACHINE MATRIX :
It is the matrix of the operator and process (machine). By this matrix, the supervisor can easily find out which operator is capable of operating which process to operate the machine. It is also called a skill matrix.

What is Retroactive Inspection in 4M change?
Retroactive inspection is to check the suspected parts that are made before any unplanned or abnormal change happens.
The record of retroactive inspection is maintained in the following format. In this format, we record the total inspection quantity, OK quantity, and rejected and rework quantities. Also maintain records of sample quantity as decided in 4M change WI.
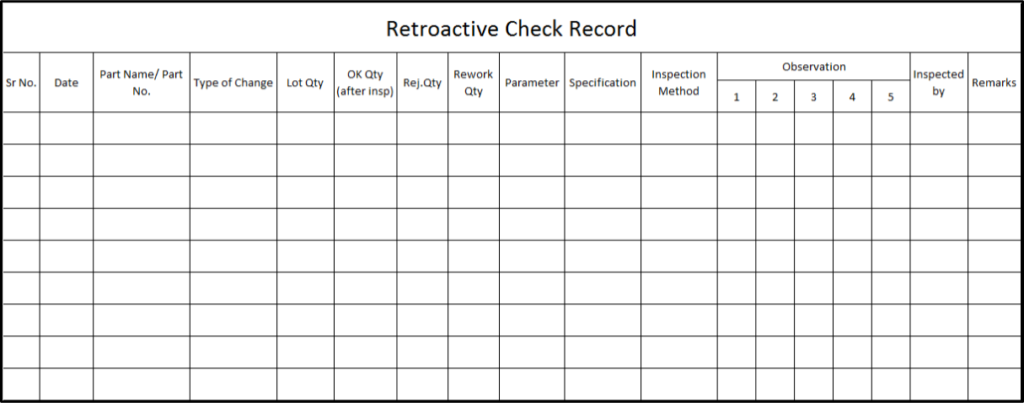
Retroactive Inspection Format:
4M CHANGE APPROVAL REPORT:
It is the Approval of the process when any process is restarted after any change happens and inspecting the sample pieces for approval. Approval should be taken from the Quality Head, Plant Head or customer.
4M Change Approval Format:
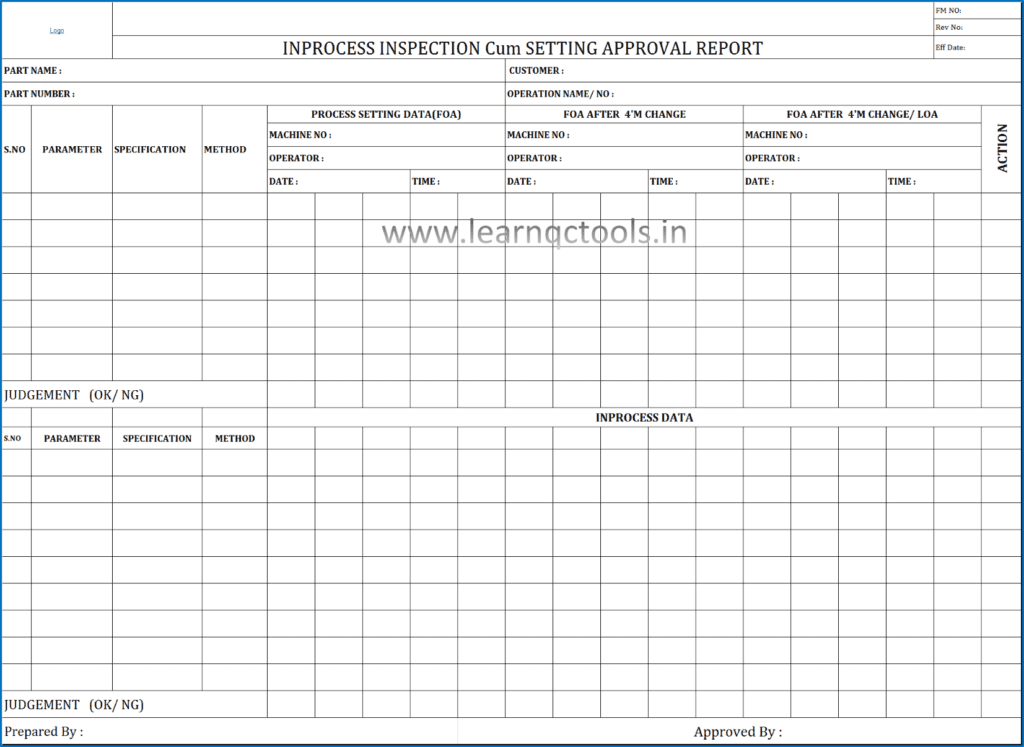
4M Change Approval Format in PDF & Excel:
4M Change Tag:
It is the tag used to identify the material that is under 4M change. It contains the details of the 4M change so that it can be traced later.
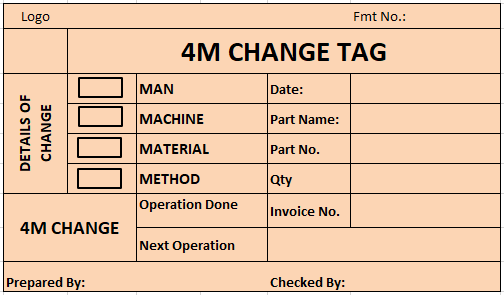
Best Practices for Effective 4M Change Control
- Maintain a centralized 4M Change Register.
- Train all process owners on when and how to raise a 4M change.
- Link your 4M change process with FMEA and Control Plan updates.
- Periodically audit 4M change records to ensure compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the 4M’s in Change Management?
The 4M’s are Man, Machine, Material, and Method – key elements of any manufacturing process.
Q2. What is the difference between planned and unplanned 4M change?
Planned changes are scheduled (like preventive maintenance), while unplanned changes are sudden (like breakdowns or tool failures).
Q3. How does 4M change help in audits?
It provides documented evidence of changes, helping trace issues and satisfy customer or auditor requirements.
Q4. What is retroactive inspection in 4M change?
It’s checking parts manufactured before an unplanned change to ensure no defective parts reach customers.
IATF 16949 Requirement related to Change Management:
Clause 8.5.6.1 Control of Changes
This clause requires the organization to implement a process for responding to unplanned changes that are considered essential to ensure that the product or service continues to meet its requirements.
The organization shall retain documented information describing the results of the review of changes. Also the person authorizing the change and any necessary action arising from the review.
- Documented process for ECN (Engineering Change Note)
- The impact of any change from the customer, organization or supplier shall be assessed
- The organization shall define the required verification after the change.
- Validate the change before implementation.
- Document the evidence of related risk analysis (PFMEA)
- Retain verification/validation record for ECN.
- Each ECN (initiated by an organization, customer or supplier) should require a production trial run for verification (PPAP)
- If required, get the customer’s approval before ECN implementation. Conduct PPAP as a customer requirement.
Reference: IATF 16949 Standard
4M change management requirements as per MSIL/MACE VSA Checksheet:
Definition and implementation of change management
Do you define unexpected change (unusual) and planned change clearly?
| Sub Questions |
|---|
| 4M change procedure defining changes, category of changes (Availability of 4M change WI) |
| Categorization of changes into planned/unplanned changes |
| Actions to be taken at the change point |
| Display of the definition of changes on the shop floor |
| Visual control of changes (4M change indication) |
| 4M Change Information rule |
| Awareness of change management among the shop floor personnel |
| Traceability system (traceability through invoice no, lot no, route card, etc.) |
Do you define procedure (rules applied from sharing information to result confirmation) at change occurrence?
| Sub Question |
|---|
| Evidence of implementation of actions: – Record of changes (4M change record), evidence of signatures of the quality and production head |
| Approval of the quality head during the 4M changes |
| Evidence of implementation |
Do you record product quality check results to ensure traceability? Include retroactive checks
| Sub Question |
|---|
| Check the record of parts produced after the change |
| Retroactive check record in case of unplanned (unexpected) changes (criteria for checking dimensional check – how many parts are to be checked dimensionally in case of retroactive check) |
| Traceability to invoice: Yes/No |
Definition and control method for the initial part:
Do you define and control the initial part clearly?
| Sub Question |
|---|
| Definition of the initial part (Up to pilot lot) |
| Initial part control – separate locked area, identification tags |
| Initial part control – log of initial parts |
Do you control initial parts separately and make quality records about them? (Both internal and outsourced processes are included)
| Sub Question |
|---|
| Separate tags to identify initial parts |
| Inspection report of initial parts |
| Separate locked area |
| Summary of initial parts prepared, sent to the customer and the balance quantity. Action taken on the balance quantity after customer feedback. |
Conclusion
Managing 4M Changes effectively is essential for automotive manufacturers to maintain quality, traceability, and customer confidence. Whether planned or unplanned, recording changes in Man, Machine, Material, and Method ensures process stability and reduces risks.
👉 Companies should use tools like Tracking Sheets, Control Boards, Skill Matrix, and Retroactive Inspections to make 4M Change Management effective and audit-ready.


found informative value added info..
Thank you for taking the time to write something that actually adds value to the conversation. This was well worth the read.
Thanks for your feedback
I understand very easily and helps to grow my knowledge. …………….Thanks for proveding a good knowledge