The purpose of the 8D problem-solving methodology is to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems, making it a valuable tool for product and process improvement.
Eight Disciplines Problem Solving (8Ds) is a method developed at Ford Motor. Quality engineers employ this methodology to resolve quality issues in the automotive industry.
- 8 Steps of the 8D problem-solving process
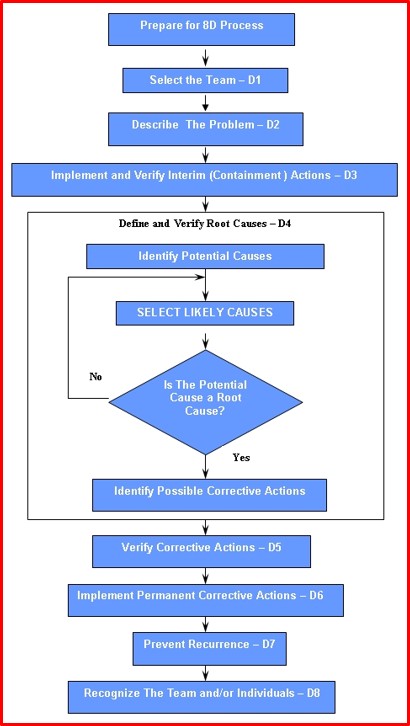
- 8D Flowchart:
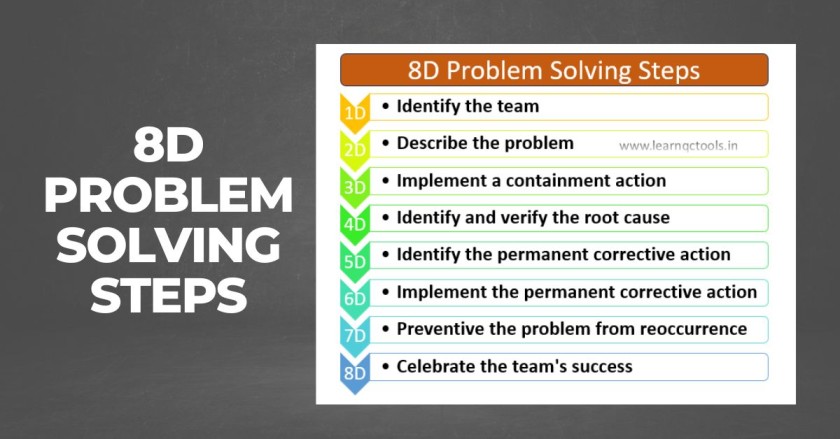
- D1: Identify and establish the team
- D2: Define and describe the problem
- D3: Implement containment actions
- D4: Determine, identify, and verify root causes and escape points
- D5: Choose and verify permanent corrections for the problem
- D6: Implement and validate corrective actions
- D7: Take Preventive measures to prevent recurrence
- D8: Recognize the team and their contribution
- Benefits of the 8D Problem-Solving Process:
- 8D Problem Solving Example | 8D Report | 8D Format
8 Steps of the 8D problem-solving process

D0: Planning and preparatory work
Before Step 1, there is a need to plan your approach. Think about who will be on the team, what the target time and what resources are required.
8D Flowchart:
D1: Identify and establish the team
Establish a small group of people with the process and product knowledge, allocated time,
authority, and skills in the required technical disciplines to solve the problem and implement
corrective actions. Key points include
- Identify the team leader and team members.
- Establish a team of competent people with product and process knowledge.
- Identify the goals and objectives.
D2: Define and describe the problem
Describe the internal or external problem by identifying “what is wrong with what” and detailing the problem in quantifiable terms. Develop a clear problem statement and problem description
- Define the problem using the 5W2H approach and Process flow diagram
- The problem definition shall be based on facts.
D3: Implement containment actions
Define, verify and implement interim containment action to isolate the effects of the problem from any
internal and external customers until permanent corrective actions are implemented.
- Containment actions are immediate actions against the problem to stop defects outflow to the customer end.
- Containment actions protect the customer’s production line from the quality problem until we define the root cause and implement necessary countermeasures.
- Examples of containment actions are: Displaying a Quality Alert Note, customer complaint awareness training to all concerned, and suspected material segregation at all stages.
D4: Determine, identify, and verify root causes and escape points
Isolate and verify the root cause by testing each root cause theory against the problem description and test data. Isolate and verify the place in the process where the effect of the root cause could have been detected and contained, but was not (escape point).
Root Cause Analysis is a systematic approach to determining and identifying the Root Cause of the problem. We can utilize seven QC tools to identify the root cause of the problem.
- Use the brainstorming and Cause-and-Effect diagrams to identify all possible causes related to your problem.
- Verify/ Validate the identified potential causes.
- Select the best potential cause that contributes to the problem.
- Find the root cause using the 5-Why approach. The real root cause will be the gap in the system, procedure and work instruction.
- Identify the root cause of both the Occurrence and Outflow.
- Verify the root cause for necessary measures.
D5: Choose and verify permanent corrections for the problem
Select the best permanent corrective actions to remove the root cause and address the escape point in the process.
- Develop a solution to remove the root cause and escape point.
- Select the best solution to remove the root cause and escape point.
- Verify the effectiveness of the selected solutions.
- Verify that selected solutions do not cause undesirable effects.
- Document and verify the permanent corrective action.
D6: Implement and validate corrective actions
Plan and implement selected permanent corrective actions and remove the interim containment action.
- Implement the best solution to remove the root cause.
- Implement the best solution to address the escape point.
- Validate the effectiveness of the implemented solutions from the Customer’s perspective.
- Monitor the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and ensure that they do not cause any undesirable effects.
- Remove Interim Containment Action
D7: Take Preventive measures to prevent recurrence
Modify the necessary systems, including policies, methods, and procedures, to prevent the recurrence of the
problem and similar ones.
- Identify opportunities to improve and standardize systems, policies, methods, and procedures for the present problem and Documents like PFD, Control Plan and FMEA to prevent a recurrence.
- Implement Poka-Yoke (error-proofing) if possible.
- Do the effectiveness monitoring of permanent corrective actions.
- Do a horizontal deployment of corrective actions.
D8: Recognize the team and their contribution
Recognize team and individual contributions. Celebrate success and identify lessons learned.
- Perform a final review of the problem-solving project.
- Recognize the team’s success and individual contributions.
- Capture lessons learned and integrate findings into the 8D Problem-solving Process.
- Congratulations to your team, Reward and celebrate.
Benefits of the 8D Problem-Solving Process:
- Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills.
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem-solving.
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures & lessons learned to prevent problems in the future.
- A better understanding of how to utilize basic statistical tools is necessary for effective problem-solving.
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency in problem-solving.
- A practical knowledge of Root Cause Analysis.
- Enhanced skills for implementing corrective action.
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change.
- Open communication in problem-solving discussions increases effectiveness.
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution.
8D Problem Solving Example | 8D Report | 8D Format
History of 8D Methodology in Ford Motor Company
The 8D methodology started at Ford Motor Company in the late 1980s. It was first known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS). Ford created it to solve quality issues in a structured way. The method uses 8 simple steps to find problems, fix them, and stop them from happening again. Ford asked its suppliers to use 8D for defects and customer complaints. Over time, 8D Problem Solving became popular worldwide. Today, it is a global standard in the automotive industry and other sectors. It improves quality, reduces defects, and increases customer satisfaction.

This is a great resource. Thank you for sharing.