The Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) is the total financial loss a company suffers because of defects, scrap, rework, customer complaints, warranty claims, poor processes, and inefficiencies. COPQ directly affects profitability, customer satisfaction, and brand reputation. Many organizations also refer to cost of quality (COQ) when analyzing their total quality costs, but COPQ specifically focuses on losses caused by “poor quality.”
In manufacturing, service, automotive, and supplier environments, COPQ is one of the most powerful tools to identify hidden losses and improve the bottom line. Understanding and reducing COPQ should be a core part of every quality management system.
What Is the Cost of Poor Quality?
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) refers to the costs incurred when a product or process fails to perform as expected. These include internal failures (scrap and rework before dispatch), external failures (customer returns and warranty), appraisal costs, and prevention costs.
COPQ full form = Cost of Poor Quality
When companies measure COPQ, they uncover the real financial impact of defects and process failures.
Difference Between COQ and COPQ
Both terms are important, but represent different concepts.
| Aspect | COQ (Cost of Quality) | COPQ (Cost of Poor Quality) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Prevention + Appraisal + Failure costs | Failure costs only |
| Purpose | Improve and maintain quality | Highlight losses due to defects |
| Focus | Total quality management | Cost of defects and poor processes |
| Better for | Continuous improvement planning | Showing actual financial losses |
COQ is broader, but COPQ focuses specifically on losses.
Types of Cost of Poor Quality
COPQ includes four major components:
1. Internal Failure Cost
Losses are found before the product reaches the customer.
- Scrap
- Rework
- Rejection
- Sorting and re-inspection
- Line stoppage due to defects
2. External Failure Cost
Losses are identified after the product reaches the customer.
- Customer returns
- Warranty claims
- Field failures
- Deduction or debit notes from OEMs
- Service/repair visits
3. Appraisal Cost
Costs incurred to evaluate, inspect, or audit products.
- Incoming inspection
- In-process inspection
- Final inspection
- Calibration
- Test equipment cost
4. Prevention Cost
Costs invested to avoid defects.
- Training
- Poka-yoke implementation
- Supplier audits
- Process improvement activities
- Preventive maintenance
Cost of Poor Quality Formula
Although COPQ varies from company to company, the common formula is:
COPQ = Internal Failure Cost + External Failure Cost + Appraisal Cost + Prevention Cost
A simplified version used by many manufacturers:
COPQ = Internal Failure Cost + External Failure Cost
Cost of Poor Quality Example
Let’s take a simple example from a manufacturing plant producing 10,000 parts per month.
- Scrap: ₹50,000
- Rework: ₹20,000
- Customer returns/warranty: ₹40,000
- Inspection/appraisal cost: ₹15,000
- Training/prevention: ₹10,000
COPQ = 50,000 + 20,000 + 40,000 + 15,000 + 10,000
COPQ = ₹1,35,000 per month
This means the company is losing ₹1.35 lakh every month due to poor quality.
Real Industry Example (Automotive/MSIL Supplier Scenario)
Assume an automotive supplier receiving 3–4 customer complaints per month (MSIL/Tier-1).
Typical losses include:
- Line rejections and sorting cost
- Customer return logistics
- Penalties or debit notes
- Extra manpower deployed
- Warranty failure cost
- Firefighting time from engineers
These hidden losses significantly increase COPQ. Many organizations discover that their actual COPQ is 5% to 20% of annual sales, once calculated correctly.
How to Calculate COPQ Step-by-Step
- Identify all quality-related cost categories
- Collect data from production, quality, stores, maintenance, and accounts
- Calculate internal failure (scrap, rework)
- Calculate external failure (warranty, customer complaints)
- Add appraisal and prevention cost
- Summarize monthly or yearly COPQ
- Compare COPQ % with sales
- Set targets to reduce COPQ every quarter
How to Reduce the Cost of Poor Quality
Here are proven methods used in successful manufacturing companies:
1. Strengthen Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Use tools:
- 5 Why
- Fishbone diagram
- 8D methodology
- Why-Why analysis
2. Implement Poka-Yoke in Processes
Simple error-proofing mechanisms drastically reduce internal rejection.
3. Improve Process Capability
Increase Cpk and reduce variation using:
- SPC
- Control charts
- Standard work
4. Upgrade Supplier Quality Performance
Supplier defects contribute directly to COPQ.
Run:
- Supplier audits
- Incoming inspection plans
- Development activities
5. Reduce Customer Complaints
Focus on recurring issues, warranty patterns, and field failures.
6. Improve Training and Skill Levels
A trained operator reduces handling defects and mistakes.
7. Strengthen Preventive Maintenance
Poor machines = poor output = high COPQ.
8. Improve Inspection and Appraisal Planning
Right inspection at the right stage prevents large rejections at the end.
Benefits of Reducing COPQ
- Improved profitability
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Reduced waste (Lean benefit)
- Better brand reputation
- Strong process control
- Lower warranty cost
- Improved supplier and customer audit rating (IATF/MSIL beneficial)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is COPQ in quality?
COPQ refers to all losses caused by poor quality, including scrap, rework, returns, warranty, and poor processes.
2. What is the full form of COPQ?
COPQ stands for Cost of Poor Quality.
3. What is the difference between COQ and COPQ?
COQ includes prevention, appraisal, and failure costs.
COPQ focuses only on the cost of defects and failures.
4. How do you calculate COPQ?
COPQ = Internal Failure + External Failure + Appraisal + Prevention.
5. Why is the cost of poor quality important?
It helps organizations identify financial losses, improve processes, reduce defects, and enhance profitability.
Purpose of COPQ:
- To reduce the cost by reducing the defect.
- To be aware of the money lost when a defect is produced in a product & detected at the in-house & customer end.
The cost of poor quality will be calculated for all rejections and rework at the in-house and customer ends. The MR/QA head will be responsible for calculating and reporting the Cost of Poor Quality.
Why Cost of Poor Quality?
If a company does not calculate COPQ, it may never know why it is incurring losses. It may also cut short inspection processes and skilled manpower, use cheap raw materials, and bypass processes to increase profit, which may ultimately lead to more quality problems.
Categories of cost of quality:
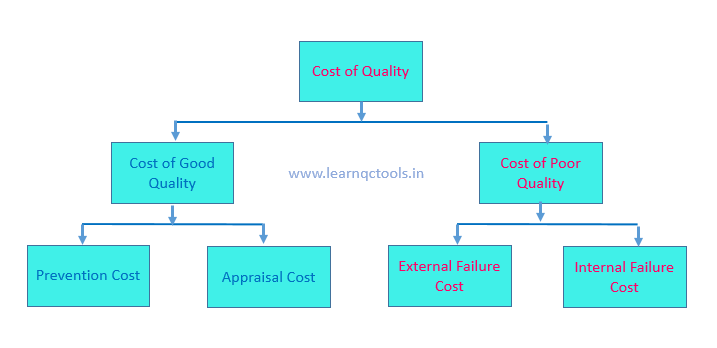
1. Prevention cost
2. Appraisal Cost
3. Internal Failure Cost
4. External Failure Cost
Cost of Good Quality:
In the Cost of Good Quality, there are included Prevention costs and Appraisal costs. It is also the cost for quality assurance.
Prevention Costs :
The cost incurred in preventing failures & reducing other costs to a minimum is called prevention costs.
- Activities of planning quality systems and translating product design & customer requirements into measures that will ensure product quality.
- The cost incurred in the product review.
- R&D testing
- Supplier assurance
- Cost includes developing & providing quality training.
- Quality system audit.
- Training employees on the quality standard
Appraisal Costs:
The cost incurred in the appraisal ( detection ) of product & process quality. It is a type of cost for quality control.
- All types of inspections. (Incoming, in process and Final inspection)
- Quality Audits and process audits.
- Calibration and maintenance of test equipment
- Laboratory testing
Cost of Poor Quality:
In cost of poor quality includes Internal failure cost and external failure cost. Here, internal failure means failure in-house in the company. External failure means failure at the customer end.
Internal Failure Costs:
Internal failure costs occur when the result of work is not as required & captured in-house.
- Scrap
- Rework and Repair
- In-house failure analysis
- Downtime of plant & machinery
- Rework and rejection of the supplier
- In-house analysis cost
External Failure Costs:
External failure cost occurs when output from an activity is not as per the requirement and captured at the customer end.
- Rework or replacement of the product
- Analysis & action taken for customer complaint
- Warranty claims
- Customer returns
- Product recall
The hidden cost of poor quality :
These are additional costs of quality that are hidden & do not appear on the COPQ calculation sheet. They are intangible and difficult to measure.
- Lost order/sale
- Loss of customers
- Management time loss
- Inventory increment
- Delivery problem
- Reputation damage
- Employee morale down
How to calculate COPQ?
The cost of poor quality will be calculated by capturing various internal and external failure costs. COPQ will normally be represented as % age of sales.
Cost of Poor Quality Formula:
Cost of poor quality percentage
COPQ% = (Total cost of Poor Quality/ Net sales of the month) x 100
where total cost includes internal failure costs and external failure costs.
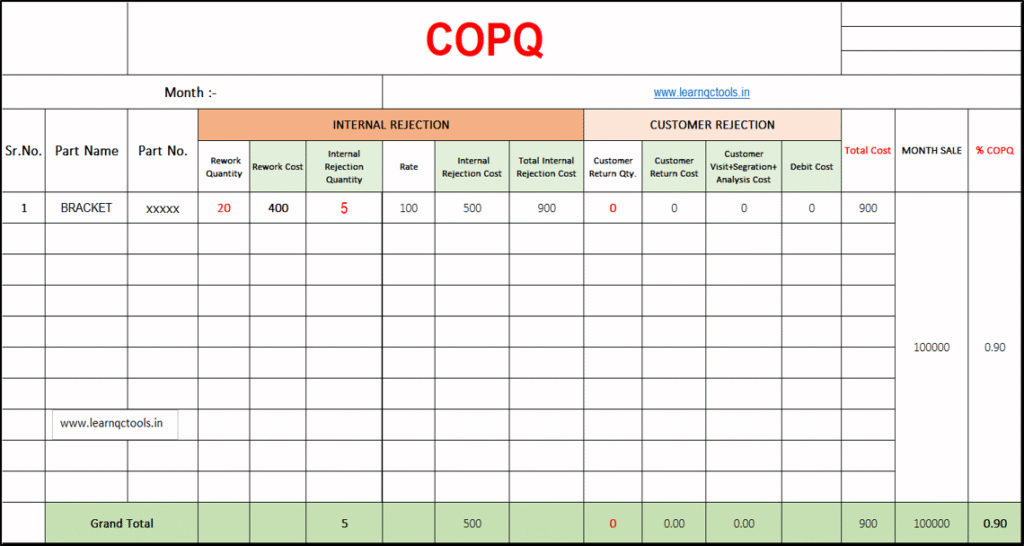
This is a simple format for capturing the cost of poor quality. They included internal failure cost and external rejection cost. Internal rejection costs include rework costs and in-house rejection costs. External rejection costs include customer return costs, customer visit costs, segregation costs, analysis and debit costs etc.
Cost of Poor Quality Format | Cost of Poor Quality Calculation Excel
Importance of COPQ in quality:
- COPQ reflects the total cost of defects, impacting profitability.
- Reducing COPQ improves overall financial performance and profit.
- High quality enhances reputation and gives a competitive edge.
- Minimizing COPQ leads to satisfied customers and loyalty.
- COPQ analysis identifies areas for process optimization.
- It helps identify and mitigate risks associated with poor quality.
- Monitoring COPQ is integral to ongoing quality enhancement.
- Managing COPQ ensures adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Conclusion
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) is not just a quality metric; it is a financial performance indicator. When companies start measuring internal failures, external failures, appraisal cost, and prevention cost, they quickly uncover major hidden wastes. Reducing COPQ is one of the fastest ways to improve profitability and strengthen the quality management system.
Every company—especially in automotive, manufacturing, and supplier environments—should track COPQ monthly and take continuous actions to bring it down.
You may like to read about


Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is fantastic, as well as the content!