Purpose:
The purpose of this procedure is to define how to manage risks & opportunities.
Scope:
This procedure covers the risks and opportunities of all processes of the organization.
Responsibility:
All the process owners are responsible for implementing this procedure.

Process Description:
Management of Risk:
Identify the risk for all the processes in the organization.
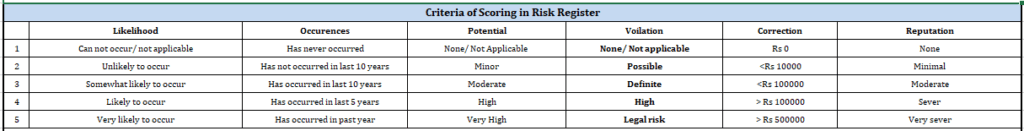
Assign a probability rating to the identified risk; this probability is comprised of two elements:
Likelihood and previous Occurrences. Each element is given a score from 1 (lowest risk) to 5 (highest risk). The final probability rating is the average of the elements.
Assign a consequence rating if the risk were to be encountered; this consequence is comprised of five elements:
- Eventual loss of contract,
- Negative impact on existing customers,
- Inability to meet contract terms,
- Any violation of statutory regulations or law,
- Impact on the company’s reputation and estimated cost of correction.
Again, each element is given a score from 1 (lowest risk) to 5 (highest risk). The final consequence rating is the average of the elements.
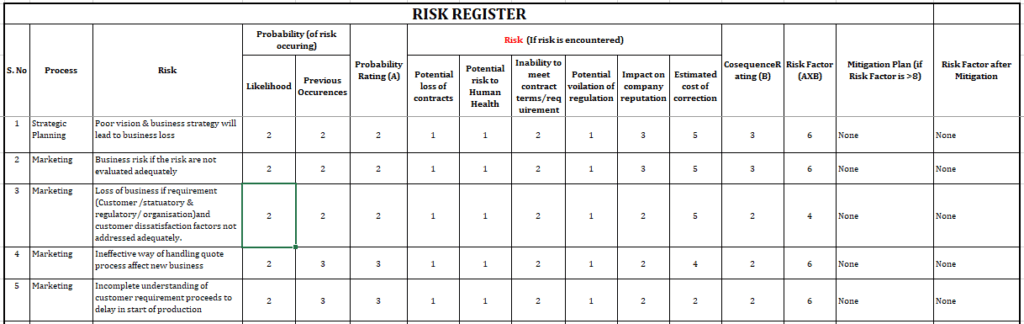
Calculate a final Risk Factor based on the equation:
Risk Factor = Probability Rating x Consequence Rating
For risks with a final Risk Factor rating equal to or greater than the threshold set in the Risk Register, decide whether to reject the subject due to the risk or accept the risks after the development of a risk mitigation plan. The mitigation plan must be documented in the Risk Register.
Risks with a factor less than the risk threshold may be accepted without a mitigation plan unless otherwise directed by management.
Enter an estimated risk factor after mitigation in the final column of the risk register, which is an estimate of what the risk should be reduced to if the risk treatment is successful.
If a risk includes a potentially positive aspect, management may choose to perform an opportunity pursuit assessment of that positive component. This is rated on a scale from 1 (lowest risk) to 5 (highest risk), with the final probability rating calculated as the average of the individual elements.”
Risk Analysis:



Management of Opportunity:
Identify the opportunity in the processes under which the opportunity most likely falls.
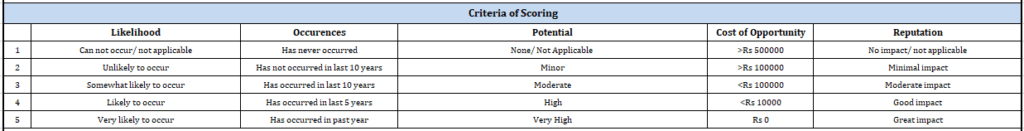
Assign a probability rating to the identified opportunity; this probability is that the organization can achieve the opportunity. It is comprised of two elements: likelihood and previous occurrences.
Each element is given a score from 1 (lowest probability) to 5 (highest probability). The final probability rating is the average of the elements.
Assign a benefit rating to assess potential benefits if the opportunity is won. This is comprised of six elements:
- Potential for new business;
- Potential expansion of current business;
- Potential improvements in the organization’s ability to satisfy regulatory or statutory requirements;
- Potential improvements to the quality management system,
- Potential enhancements of the company’s reputation and the estimated cost of implementation.
Again, each element is given a score from 1 (lowest benefit) to 5 (highest benefit). The final benefit rating is the average of the elements.
Calculate a final Opportunity Factor based on the equation:
Opportunity Factor = Probability Rating x Benefit Rating
For opportunities with a final Opportunity Factor rating equal to or greater than the threshold set in the Opportunity Register, decide whether to pursue the opportunity through an “opportunity pursuit plan” or to abandon the opportunity altogether. The opportunity pursuit plan must be documented in the Opportunity Register.
Opportunities with a factor less than the opportunity target rating may be abandoned outright unless otherwise directed by management.
Enter the success result, once the opportunity has been closed; this includes entries for abandoning the opportunity, failing to win the opportunity, and three grades of success.
If an opportunity includes a negative aspect, management may elect to conduct a risk assessment on the negative aspect, as defined above.
Opportunity Analysis:


Risk Analysis of all processes in the organization should be done as FMEA is done & actions are taken.
You may like to read about,
List of mandatory procedures for IATF 16949.


Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.