Overall Equipment Effectiveness, commonly known as OEE, is one of the most important performance indicators used in Lean Manufacturing to measure how efficiently manufacturing equipment is utilised. OEE helps organisations identify losses, improve productivity, reduce downtime, and increase output without additional investment. In automotive, engineering, and process industries, OEE is widely used as a core metric under TPM, Kaizen, and IATF 16949 continual improvement systems.
Many companies calculate OEE but fail to use it effectively due to incorrect definitions, poor data collection, or a misunderstanding of its purpose. This article explains how to calculate OEE in Lean manufacturing, using clear definitions, formulas, practical shopfloor examples, common mistakes, benchmarks, and implementation best practices.
- What is OEE in Lean Manufacturing?
- Why OEE is Important in Lean Manufacturing
- OEE Formula Explained
- Key Terms Used in OEE Calculation
- Step-by-Step OEE Calculation in Lean Manufacturing
- Step 1: Calculate Availability
- Step 2: Calculate Performance
- Step 3: Calculate Quality
- Step 4: Calculate OEE
- OEE Calculation Summary Table
- What is a Good OEE Value?
- OEE and the Six Big Losses
- Common Mistakes in OEE Calculation
- How to Implement OEE on the Shopfloor
- OEE in TPM and Continuous Improvement
- OEE and IATF 16949 Requirements
- Difference Between OEE, Efficiency, and Productivity
- Frequently Asked Questions on OEE
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) calculation :
- OEE Calculation Example:
- OEE Calculation Excel Sheet
- Conclusion:
What is OEE in Lean Manufacturing?
OEE stands for Overall Equipment Effectiveness. It measures how effectively a manufacturing process operates compared to its full potential during planned production time. OEE provides a single percentage value that reflects the true productivity of a machine or process.
OEE is not just a number. It is a diagnostic tool that highlights where losses occur and supports data-driven decision-making in Lean Manufacturing.
OEE consists of three components:
Availability
Performance
Quality
OEE answers one key question:
How much of the planned production time is actually used to produce good parts at the right speed?
Why OEE is Important in Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and maximising value. OEE directly supports this objective by identifying losses related to equipment and processes.
Benefits of using OEE include:
- Identification of hidden losses
- Improved equipment utilisation
- Reduced downtime and breakdowns
- Better production planning
- Higher product quality
- Stronger TPM and Kaizen implementation
For automotive suppliers and IATF 16949 certified organisations, OEE also provides objective evidence of process performance monitoring and continual improvement.
OEE Formula Explained
The standard OEE formula is:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
Each factor represents a different category of loss. When multiplied together, they give the overall effectiveness of the equipment during planned production time.
Key Terms Used in OEE Calculation
Correct OEE calculation starts with clear and consistent definitions. The following terms must be understood and agreed upon across production, maintenance, and quality teams.
Planned Production Time
This is the time during which production is scheduled to run. Planned breaks such as lunch breaks, tea breaks, and planned maintenance are excluded.
Run Time
Run Time is the actual time the machine is running. It is calculated by subtracting unplanned downtime from Planned Production Time.
Unplanned Downtime
Any event that stops production unexpectedly, such as breakdowns, tool failure, material shortage, power failure, or operator absence.
Ideal Cycle Time
The minimum time required to produce one part under ideal conditions. This should be based on machine capability, not average performance.
Total Count
The total number of parts produced, including defective parts.
Good Count
The number of defect-free parts that meet quality requirements.
Step-by-Step OEE Calculation in Lean Manufacturing
To make OEE easy to understand and implement, it should be calculated step by step.
Step 1: Calculate Availability
Availability measures losses due to stoppages.
Availability Formula
Availability = Run Time ÷ Planned Production Time
Availability losses are caused by equipment failures, setup delays, tool change delays, and unplanned stoppages.
Example
Planned Production Time = 480 minutes
Unplanned Downtime = 60 minutes
Run Time = 480 − 60 = 420 minutes
Availability = 420 ÷ 480 = 0.875 or 87.5%
Step 2: Calculate Performance
Performance measures losses due to slow running and minor stops.
Performance Formula
Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Count) ÷ Run Time
Performance losses occur when machines run below their design speed or experience frequent small stoppages.
Example
Ideal Cycle Time = 1 minute per part
Total Parts Produced = 380
Run Time = 420 minutes
Performance = (1 × 380) ÷ 420 = 0.905 or 90.5%
Performance should never exceed 100%. If it does, the Ideal Cycle Time definition is incorrect.
Step 3: Calculate Quality
Quality measures losses due to defects and rework.
Quality Formula
Quality = Good Count ÷ Total Count
Quality losses occur due to process variation, tool wear, setup issues, or material defects.
Example
Total Parts Produced = 380
Defective Parts = 20
Good Count = 360
Quality = 360 ÷ 380 = 0.947 or 94.7%
Step 4: Calculate OEE
OEE Formula
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
OEE = 0.875 × 0.905 × 0.947
OEE = 0.75 or 75%
This means that only 75% of the planned production time is truly productive.
OEE Calculation Summary Table
Availability = 87.5%
Performance = 90.5%
Quality = 94.7%
OEE = 75%
This breakdown helps teams understand exactly where losses are occurring.
What is a Good OEE Value?
OEE benchmarks vary by industry, but general Lean Manufacturing standards are:
Below 60% – Poor performance
60% to 70% – Average
70% to 85% – Good
Above 85% – World-class
World-class OEE of 85% is challenging and usually achieved only with strong TPM systems, stable processes, and disciplined maintenance.
OEE and the Six Big Losses
OEE is directly linked to the Six Big Losses in Lean Manufacturing.
Availability Losses
Breakdowns
Setup and adjustment
Performance Losses
Minor stoppages
Speed loss
Quality Losses
Startup defects
Production defects
By mapping OEE losses to the Six Big Losses, organisations can systematically eliminate waste.
Common Mistakes in OEE Calculation
Many companies fail to get correct OEE results due to the following mistakes:
Including planned breaks in Planned Production Time
Ignoring micro stoppages
Using average cycle time instead of ideal cycle time
Allowing Performance to exceed 100%
Calculating OEE without verifying data accuracy
Using OEE only for reporting, not improvement
Correct definitions and consistent data collection are critical for meaningful OEE analysis.
How to Implement OEE on the Shopfloor
To successfully implement OEE in Lean Manufacturing, follow these best practices.
Start with one critical machine
Define terms clearly and document them
Collect data manually or digitally at the shift level
Review OEE daily with operators and supervisors
Focus on improving one loss at a time
Use root cause analysis tools such as Pareto, Why-Why, and Fishbone
Integrate OEE review into daily management meetings
OEE should be visible on the shopfloor through boards or dashboards.
OEE in TPM and Continuous Improvement
OEE is a core metric in Total Productive Maintenance. It supports TPM pillars such as Autonomous Maintenance, Planned Maintenance, and Focused Improvement.
OEE trends help maintenance teams move from reactive maintenance to preventive and predictive maintenance.
In Kaizen activities, OEE data provides factual evidence of improvement results.
OEE and IATF 16949 Requirements
In IATF 16949, organisations are required to monitor and measure manufacturing process performance. OEE supports compliance with clauses related to:
- Process performance monitoring
- Continual improvement
- Risk-based thinking
- Maintenance effectiveness
Auditors often expect to see OEE data analysis, improvement actions, and result tracking.
Difference Between OEE, Efficiency, and Productivity
OEE is often confused with efficiency or productivity, but they are not the same.
Efficiency typically compares actual output to planned output.
Productivity focuses on output per resource.
OEE measures true equipment effectiveness by combining availability, speed, and quality.
OEE provides deeper insight than traditional efficiency metrics.
Frequently Asked Questions on OEE
What is the full form of OEE?
OEE stands for Overall Equipment Effectiveness.
How often should OEE be calculated?
OEE should be calculated shift-wise or daily for effective control.
Can OEE be more than 100%?
No, OEE cannot exceed 100%. If it does, the input data or ideal cycle time is incorrect.
Is OEE applicable to manual processes?
OEE is primarily designed for equipment-based processes, but similar concepts can be adapted for manual operations.
Is OEE mandatory in IATF 16949?
OEE is not mandatory, but it is a widely accepted best practice for process performance monitoring.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) calculation :
OEE is the product of Availability, Performance and Quality. OEE is calculated as a percentage.
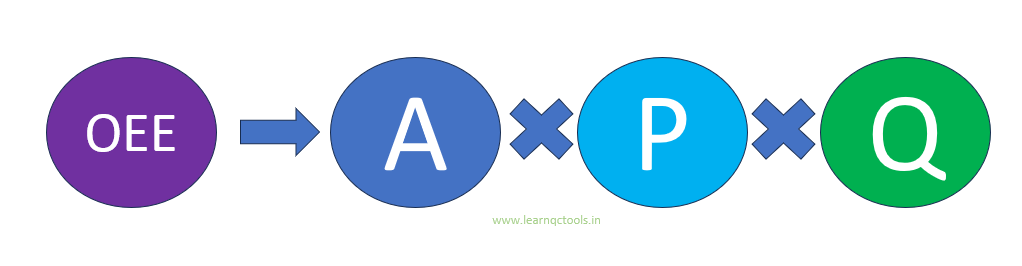

OEE % = Availability % x Performance % x Quality %
OEE Calculation Example:
Calculate OEE by considering a shift of 8 hrs, Machine breakdown of 30 minutes, Total production of 3800 parts and rejection of 20 parts and the target as per cycle time is 4000 parts.
Availability = ((Total available time – Breakdown time) / Total available time) x100
Availability = ((480 – 30) / 480)*100 = (450 / 480)x100 = 93.75%
Performance = Production Quantity / ( Net available time x Cycle Time ) x 100
Performance = (3800 / 4000) x100= 95%
Quality = (Total OK Products / Total Production) x 100
Quality = (3780 / 3800) x100 = 99.47%
OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality
OEE = 93.75% x 95% x 99.47% = 88.59%
OEE Calculation Excel Sheet
Download the OEE Excel Sheet
Update the data date-wise as per the format.
Conclusion:
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a lean manufacturing tool and universal best practice to monitor, evaluate and improve the effectiveness of a production process. This could be an assembly line, machine cell, packaging line etc. But it can also be considered a strong financial indicator. When expressed in monetary terms, the OEE metric can be used to illustrate the potential economic impact of optimising production and justify investments to increase efficiency in your plant.
OEE is a powerful Lean Manufacturing tool that reveals how effectively equipment is being used. When calculated correctly and analysed consistently, OEE helps organisations identify losses, improve equipment reliability, and enhance overall productivity.
Instead of focusing only on achieving a high OEE number, organisations should focus on reducing Availability, Performance, and Quality losses step by step. When used as an improvement tool, OEE becomes a strong foundation for TPM, Lean Manufacturing, and operational excellence.
You may like other lean tools: Jidoka in lean manufacturing,
What is Poka Yoke (Error Proofing)?


Thanks for fantastic info I was looking for this information for my mission.