Cycle Time vs Takt Time:
Cycle Time:
Cycle time in manufacturing is the time taken to produce a final part using different processes. It is a time-consuming process that takes the maximum time. We can get cycle time by observing the process for a defined time and counting the number of parts produced. We should make observations at different times and average them. With this quality objective (KPI), we can measure the productivity of the manufacturing process.
Takt Time:
Takt time is the required time to produce one unit as per customer demand. It sets the rate of production to match the rate of customer demand. Takt time is an element of lean manufacturing.
Takt Time = Available Production Time / Rate of customer demand

How to calculate takt time? | Takt time example :
What is the takt time if 1000 units are needed per day, and the company has 10-hour shifts? Also consider lunch 30 minutes, 2 tea breaks of 10 minutes, 30 minutes for other personal breaks, and 2 breaks for machine cleaning of 10 minutes each.
Total shift hours = 10 hrs (10 x 60=600 min)
Lunch = 30 min
Tea Break = 20 min ( 2 x 10 min)
Other Break = 30 min ( 3 x 10 min)
Machine Cleaning = 20 min (2 x10 min)
Total breaks = 30+20+30+20 = 100 minutes
Net Available Time = 600 – 100 = 500 minutes
Customer demand = 1000 Units
Takt Time = Available Time / Customer demand
= 500 /1000 = 0.5 min = 30 second
So to meet customer demand, we have to make two parts per minute.
Cycle time should be less than takt time to meet customer demand. If the cycle time is more than the takt time in a machine or line. Then we can manufacture that part with more machines or lines.
But in actuality, operators can never achieve 100 % efficiency, so we need to provide some allowances by considering some other stoppages.
What are the benefits of the takt time?
Below are the benefits of balancing takt time and cycle time:
- Control of production: Takt time stabilizes the system & controls over-production.
- Performance increase: Feedback on performance works as a motivating factor. When operators work as per takt time, their output increases. They try to achieve takt time & make the required planning & solutions.
- Line Balancing: Takt time helps the process designers to make line balancing.
What happens if takt time is more than cycle time?
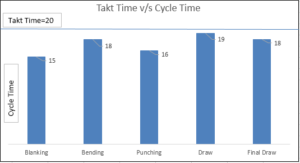
In this case, a sheet metal part is produced through these processes. Cycle Time ( highest is 19 sec) is just below the Takt Time (20), So customer demand will be met. There is no need to take action immediately. Further, we can improve by balancing the cycle times of processes to complete the product of that part.
What happens if the cycle time is more than the takt time?
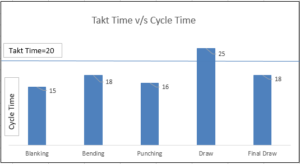
In this case, the operation Draw operation (25 sec) exceeds Takt time (20 sec), so customer demand can not be met. So there is a need for overtime to fulfill the customer demand. Also there will be other losses like loss of sale, the customer will be dissatisfied, increase in freight charges. There will be a need to take action (Kaizen) on the process having a cycle time more than takt time.
What are the limitations of takt time?
Takt time is used for simple processes. It applies to the processes that are
- Minimum setups
- Single routing
- Similar cycle time for all products
It is difficult to apply to low-volume & high-variety operations.
You may like to read about other lean manufacturing tools:
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
Value Stream Mapping (VSM)

