In the manufacturing industry, quality control plays a vital role in ensuring that products meet customer requirements and regulatory standards. A well-defined quality control process helps prevent defects, reduce rework, and improve customer satisfaction.
This article explains the quality control process in manufacturing in a practical and easy-to-understand way, focusing on incoming material inspection, in-process inspection, final inspection, reports, and key benefits.
- What is Quality Control in Manufacturing?
- Why Quality Control is Important in Manufacturing Industry
- Incoming Material Inspection in Quality Control
- In-Process Inspection in Manufacturing
- Final Inspection in Quality Control Process
- Final Inspection Procedure in Manufacturing
- Quality Control Inspection Types – Comparison
- Quality Control Inspection Reports and Records
- Benefits of Quality Control in Manufacturing Process
- Quality Control Process Steps:
- Incoming Material Inspection Procedure (Raw Material, Bought Out Parts, Job Work) :
- In-Process Inspection procedure:
- Final Inspection procedure:
- Conclusion: Effective Quality Control in Manufacturing
What is Quality Control in Manufacturing?
Quality control in manufacturing is a systematic process of monitoring, inspecting, and testing products at different stages of production to ensure they conform to specified requirements.
Quality control focuses on detecting defects early, controlling process variation (SPC), ensuring consistent product quality, and meeting customer and statutory requirements.
Quality control activities are usually carried out at three main stages: incoming material inspection, in-process inspection, and final inspection.
Why Quality Control is Important in Manufacturing Industry
Effective quality control is important because it reduces rejection, rework, and scrap, improves customer satisfaction and trust, ensures compliance with quality standards (ISO 9001 Requirements), helps in cost reduction by preventing defects, and improves process stability and consistency.
A strong quality control system supports long-term business growth and competitiveness.
Incoming Material Inspection in Quality Control
Incoming material inspection is the first step in the quality control process. It ensures that raw materials, components, or purchased parts received from suppliers meet specified requirements before being used in production.
The purpose of incoming material inspection is to verify supplier quality, prevent defective material from entering production, and ensure compliance with specifications and drawings.
During incoming inspection, checks typically include visual condition, dimensional characteristics, material grade or specification, and supplier certificates or test reports where applicable.
Records maintained include incoming inspection reports and material acceptance or rejection records. Supplier Control procedure is followed for incoming inspection.
In-Process Inspection in Manufacturing
In-process inspection is carried out during manufacturing operations to ensure that the process remains under control and products meet requirements at each stage.
The purpose of in-process inspection is to detect defects early during production, control process variation, and prevent defects from reaching final inspection.
In-process inspection is usually conducted at defined stages or intervals and may include dimensional, visual, or functional checks. It is often linked with control plans and work instructions.
An in-process inspection report typically includes the operation or process stage, characteristics inspected, inspection method and frequency, acceptance criteria, and inspection results.
Final Inspection in Quality Control Process
Final inspection is the last stage of quality control before products are dispatched to the customer. It confirms that finished products meet all specified requirements.
The objective of final inspection is to ensure product conformity, confirm compliance with drawings and specifications, and prevent non-conforming products from reaching customers.
Final inspection is performed after completion of all manufacturing operations and before packing and dispatch, usually by authorized quality inspectors or quality personnel.
Final Inspection Procedure in Manufacturing
A typical final inspection procedure in manufacturing includes reviewing product drawings, specifications, and inspection plans, selecting samples as per the defined sampling plan, performing visual inspection for surface defects and workmanship, conducting dimensional inspection using calibrated instruments, carrying out functional or performance checks where required, recording inspection results in the final inspection report, and approving or rejecting the product based on inspection results.
Following a standardized final inspection procedure ensures consistency and reliability.
Quality Control Inspection Types – Comparison
Incoming inspection is carried out before production to verify supplier quality, and records are maintained in incoming inspection reports.
In-process inspection is carried out during production to control process variation, and records are maintained in in-process inspection reports.
Final inspection is carried out after production to confirm product conformity, and records are maintained in final inspection reports.
This structured approach ensures quality control throughout the manufacturing process.
Quality Control Inspection Reports and Records
Inspection reports and records provide evidence that quality control activities have been performed effectively.
Common quality control records include incoming material inspection reports, in-process inspection reports, final inspection reports, non-conformance reports, and corrective action records.
These records are important for internal control, audits, and customer confidence.
Benefits of Quality Control in Manufacturing Process
Implementing an effective quality control process improves product quality and consistency, reduces manufacturing losses, increases customer satisfaction, improves compliance with quality standards, and enhances overall process efficiency.
Quality control helps organizations move from defect detection to defect prevention.
Quality Control Process Steps:
- Incoming inspection
- In-process inspection
- Final Inspection
Incoming Material Inspection Procedure (Raw Material, Bought Out Parts, Job Work) :
- Receive goods inward receipt (GIR) from the store
- Select a sample, inspect the material and prepare an inspection report
- If part OK, Clear GIR and send to store
- In the case of NG, Forward the inspection report to the Head QC
- Review the inspection report and mark the decision
- Reject / Accept under deviation /Hold /Rework/Segregation
- Raise a quality problem countermeasure report QPCR to the supplier as per supplier rejection criteria and ensure required action(s) are taken by the supplier: Sort the material at our works. Rectify the material at our works. Collect rejection back
- If rejected or accepted under deviation, decide on GIR if held. Mark the decision on GIR Rework/Segregate.
- Get the material reworked/segregated by the supplier or in the plant.
- Inspect the reoffered material after rework/segregation.
- Follow up with a supplier in case of QPCR sent
- After receipt of QPCR, monitor the effectiveness of countermeasures.
Incoming Material Inspection Format:
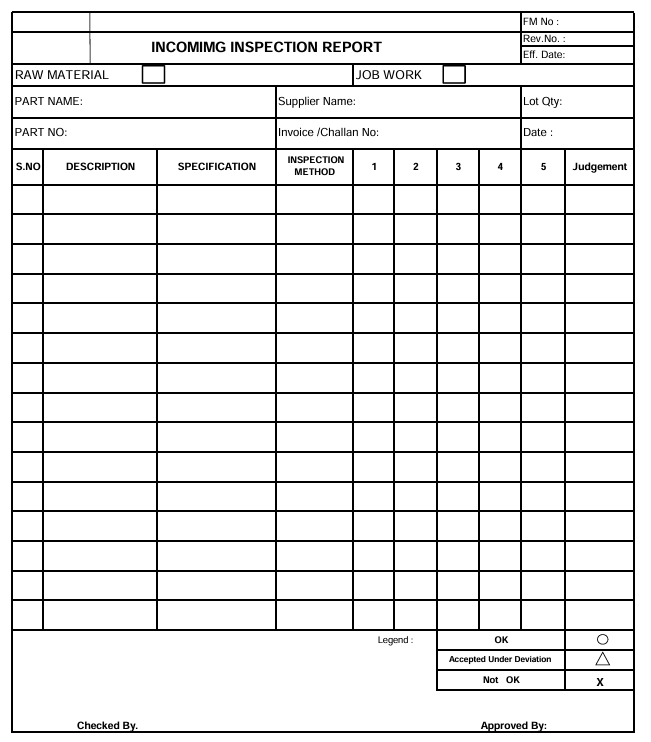
In-Process Inspection procedure:
- Submit initial samples from production
- Inspect samples on the Patrol inspection report (PIR)
- If the sample is NG, then put the NG setting parts in the red bin.
- Reset the machine/tool as per the maintenance procedure.
- Resubmit the sample for inspection.
- If the sample is OK after inspection, then verbally inform the operator / Shop in charge to start production.
- Mark the OK sample with a sign and date.
- Provide the signed OK sample to the operator to store on the machine at the designated location.
- Check the parts and process as per the inspection frequency decided in the control plan.
In-process Inspection report format:
You may also like Quality Control vs Quality Assurance
Final Inspection procedure:
- Receive information (after packaging)
- Inspect items to be dispatched as per the final inspection standard. If OK then
- Approval for dispatch (to Head Manufacturing)
- Forward the Final inspection report to the Head QC
- Review Final inspection report / Re-offer for Inspection / Rejection / Concessional approval
- If rejected or concessional approval/identify material / Convey status.
- If rework & re-offer for inspection. Identify material. Convey status to the Manufacturing Head.
Final Inspection Report Format:
Conclusion: Effective Quality Control in Manufacturing
Quality control is an essential part of the manufacturing process. By implementing incoming material inspection, in-process inspection, and final inspection with defined procedures and proper records, organizations can ensure consistent product quality.
A structured quality control process not only improves product reliability but also strengthens customer trust and long-term business performance.

