Stratification
Stratification is the separation of data into categories. This tool is usually used to identify which categories contribute to the problem during the diagnostic process. We can separate data into different categories so that the data of that category can be observed to solve the problem.
Stratification is a system of formation of categories, classes or layers. Data collected by check sheet need to be meaningfully classified. Such categorization helps in understanding the data so that further analysis can be done to get the proper result. This tool separates the data so that patterns can be seen.
A category is defined by a specific combination or range of variables. In a category, there is more than one variable. Stratification by itself does not point out the root cause of the problem. It helps to sort out which areas need further investigation. Stratification is the base of other tools like Pareto analysis, scatter diagrams etc.
What is the use of stratification?
- To categorize data from different sources like machines, operators, dates, and suppliers.
- Stratifying customer complaints by type of complaint or type of customer can help in identifying the important problems.
- It is useful in focusing the investigation on the most serious symptoms and indicating where to look for the root cause.
- Stratification help in testing theories in the case of cause and effect diagram.
- It is useful to stratify data on the new performance level by the variable used during the diagnostic process.
Importance of stratification in quality control
- It ensures all subgroups are added and their accuracy
- It identifies variations in each sub-group.
- It minimizes error compared to random sampling
- It ensures easy and cost-effective quality control
- Identify higher risk area
- Addresses specific quality issues
What are the precautions in the use of stratification?
- Small differences between data classes should not be taken into consideration.
- It should not be considered that the abnormal category is the cause of the problem.
- When there is a need to collect new data, there must be an effort to collect as much identifying information as required for stratification.
How to stratify?
Step 1: Select the stratification variables: When new data are collected, make sure that all potential stratification variables are included like a machine, operator, date etc.
Step 2: Establish categories for each stratification variable: A category is a value or range of value of a stratification variable. For example dates of the month are 1 to 31.
Step 3: Sort observations into categories of one of the stratification variables.
Step 4: Calculate the phenomenon measured for each category. Collect the data date-wise.
Step 5: Display the result. Usually graphic displays are the most effective.
Step 6: Prepare and display the results for additional stratification variables.
Step 7: Plan for additional confirmation.
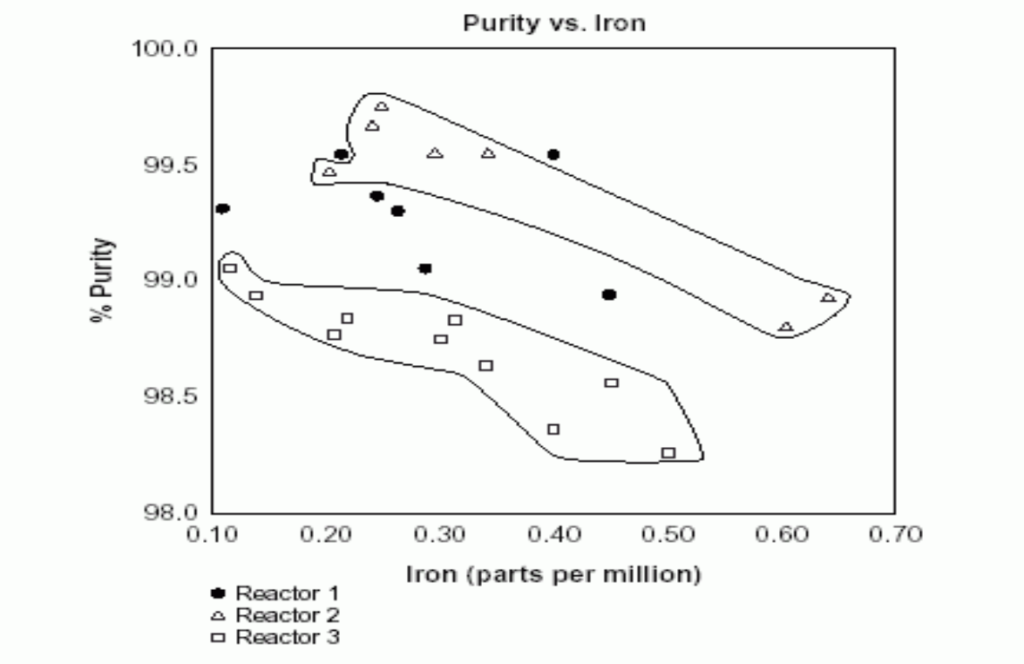
How to interpret stratification?
It is usually best to present the stratification result in graphic form. If the stratification results are in bar graph form. It will be easy to see the categories of the variables to see whether one or more of the categories stand out.
- Does one machine has a higher defect rate?
- Does one operator have a higher defect rate?
- Is the shift or specific date the reason for the high defect rate?
After stratification, if the result provides a clear indication of the likely source of the phenomenon being studied. Then the team has to validate their initial result. If we do not get any useful results then see the other variables with each category.
You may like to know about the Pareto Chart, Scatter Diagram and Check Sheet.
Stratification in quality control example:
Stratification in quality control is a process used to categorize and analyze data based on certain characteristics. An example of stratification in quality control could be as follows:
Suppose a company produces 1000 units of a certain product per day. The company wants to ensure that the quality of the products meets the required standards. To achieve this, the company samples 100 units randomly from the 1000 units produced and performs various quality tests on each unit. The results of the quality tests are then recorded and analyzed.
To stratify the data, the company categorizes the 100 units into groups based on certain characteristics, such as production date, shift, or operator. This way, the company can identify trends or patterns in the data and determine if there are any significant differences between the groups.
For example, suppose the company stratifies the data based on production date. The company discovers that the units produced on a certain day have a higher rate of defects compared to the units produced on other days. This information allows the company to focus its efforts on identifying and addressing the root cause of the increased defects on that particular day.
In this way, stratification in quality control can help a company identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to ensure consistent quality in its products.

Glad I observed this on google .