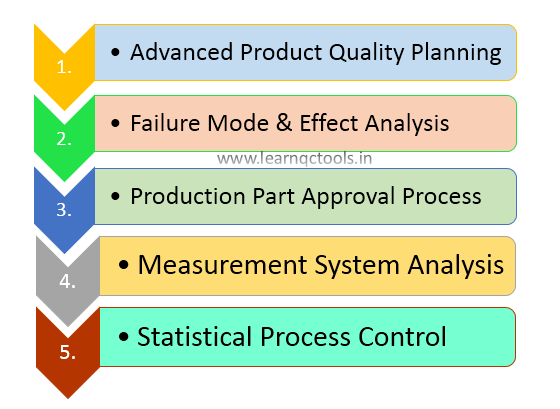
The 5 Core Tools are the 5 supplemental tools that support the requirements of IATF 16949. These 5 core tools are published separately in five manuals available by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG). These are also called 5 quality core tools. Below the five core tools are listed when designing products or processes during new development.
- Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA)
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Advanced Product Quality Planning:
APQP is a process of facilitating communication with all concerned within the organization and also with Suppliers and Customers for ensuring that all required steps are completed on time. APQP activities include various stages of development of Prototype/Product sample, Pre-launch, Production and Mass production from receipt of order to SOP at the customer end. There are 5 Phases in the APQP process:
5 Phases of APQP:
- Plan and define phase
- Product design & development
- Process design & development
- Product and process validation
- Feedback assessment & corrective action
Failure Mode & Effect Analysis:
FMEA is a synchronized group of activities that are intended to recognize and evaluate the potential failure of a product/process & its effects. FMEA is a methodology used to ensure that potential problems have been analyzed, considered and addressed in any product and process development process.
- Identify actions that could determine or reduce the chance of the potential failure occurring.
- To document the process
You may like to know about AIAG VDA FMEA
Production Part Approval Process:
PPAP is a process to provide evidence that all customer engineering design records & specifications requirements are properly understood by the organization. The manufacturing process has the potential to produce the product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate.
There are 18 elements of PPAP:
- Design Record / Drawing
- Authorized Engineering Change Documents
- Design Failure Mode & Effect Analysis
- Process Flow Diagram
- Process Failure Mode & Effect Analysis
- Control Plan
- Measurement System Analysis
- Dimensional results
- Records of material / Performance tests
- Material test report
- Initial Process Studies (SPC)
- Qualified Laboratory documents
- Appearance approval report
- Sample production parts
- Master sample
- Checking aids
- Customer-specific requirements
- Part Submission Warrant ( PSW)
Measurement System Analysis:
A measurement System is the collection of instruments, standards, operations, methods, fixtures, software, inspectors, environment & assumptions used to quantify a unit of measure or fix assessment to the feature characteristics being measured. It is the complete process used to obtain a measurement during measurement system analysis. It is one of the 5 core tools.
Measurement system analysis primarily deals with consulting the effect of the measurement system on the measured value. The objective of MSA is accessing the quality of the measurement system. We test the system to determine its statistical properties and use them in comparison with accepted standards, our needs & customer requirements.
- Bias
- Stability
- Linearity
- Repeatability
- Reproducibility
Statistical Process Control:
SPC is controlling the process variation by using statistical techniques. Statistical techniques such as Control charts and Histograms are used so as to analyze the process & achieve & maintain a state of statistical control to get a product having no defect.
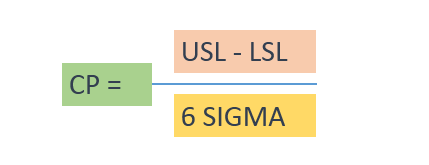
Process Capability:
It is the measurement of the inherent variation of the process when it is in stable condition with respect to process specification.
Cp = (USL – LSL) / 6 sigma
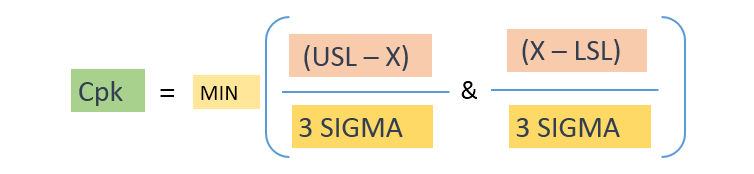
Process Capability Index:
The process capability index is the measurement of process capability. It defines how close a process is able to produce the product to the specifications.
Cpk = Min ( (USL – Mean)/3 Sigma & (Mean – LSL)/3 Sigma)


Amazing! Its in fact amazing post, I have got much clear idea about
from this post.