Management review of the organization’s QMS at planned intervals will be done by top management. Management review is done to ensure the continuing suitability, adequacy, effectiveness and alignment with the strategic direction of the organization.
Input/checkpoints to be discussed during MRM:
Below is the IATF Management Review Checklist:
1. Status of actions from previous management review:
If no specific action is pending from the last MRM, then it is OK. If any action is pending for the previous MRM, then review its progress. Take action to close that point immediately.
2. Change in external and internal issues that are relevant to the QMS:
Verify that if any change in the issue of all interested parties. Then take action to close that issue. If no change, then it is OK.
3. Customer satisfaction and feedback from relevant interested parties:
Review the scorecard received from all customers. If not received, then ask customer satisfaction report from the customers. If it is less than the target in any month, then review the action taken and the closure. If the customer does not provide the report, then prepare the customer satisfaction report as per available data. The customer satisfaction target should be 100%.
4. Quality Objective achievement status:
Review the Key Performance Indicator ( KPI ) of each department against the target. If found less than the target, then take action accordingly.
5. Process performance and conformity of products and services:
Do a product and process audit as per the plan with a product and process audit check sheet. Close all observations within the time limit.
6. Nonconformity and corrective actions:
a) Customer Complaint:
Review complaints of all customers of the last 6 months ( From the last MRM). There should not be any repetitive customer complaints.
b) In-house Rejection PPM:
Review the in-house rejection ppm of the last 6 months against the target. If it is within target, then OK. If rejection PPM is above the target, then take action accordingly. In-house rejection PPM will be captured through the Red bin analysis process.
7. Monitoring and measurement results:
Verify Monitoring and measurement resources, their calibration record and measurement system analysis (MSA)
8. Audit results:
a) Internal Audit:
Internal audit was conducted following IATF 16949 standard during this period ( from…. to…..) as per the schedule prepared by MR and all departments have been covered during the audit. The following NCs were reported during the audit and all are minor. Found that there is no repetition of the same NCs.
Action Plan: Analysis has been carried out for all the NCs and correction and corrective actions have been taken. All these NCs have been closed after verification of actions by the respective auditors. To ensure that there is no repetition of these NCs in the future. The status of the effectiveness of actions taken is to be reviewed in the next MRM.
b) Process & Product Audit:
The following processes were taken up for process audit as per the plan in the last 6 months.
Action Plan: Actions have been taken on all the observation points reported during the process audit. The concerned process owner is to ensure that these observations are not repeated in the subsequent audits.
Process Audit is done as per the Process Audit Check Sheet, covering all processes and all shifts once a year.
c) External Audit:
Mention the details of the audit done by all the customers, IATF certification bodies like BSI, TUV, DNV etc.
Action Plan: Actions have been taken on all the observation points reported during the customer audit. The concerned department head is to ensure that these observations are not repeated in the subsequent audits.
How to close the IATF 16949 audit NC on the NC CARA Portal.
d) Supplier Audit:
Supplier audits have been carried out as per the plan during the period. Make a list of the suppliers for the audits carried out last 6 months.
Action Plan: Actions have been taken on all the observation points reported during an audit of the supplier. Closure evidence is collected from the supplier. The supplier has to ensure that these observations are not repeated in the subsequent audits
9. Performance of external providers:
Supplier rating is calculated as per the criteria every month for all suppliers. Review the supplier rating as per the target. If the rating of any supplier is less than the target, then take action as per the supplier control procedure.
10. The adequacy of resources:
Review the requirements of any resources and also discuss the added resources in this period
11. Effectiveness of action taken to address risk and opportunities:
Review the Risk and Opportunity identified. For some of the risks identified in risk assessment, actions have been taken to prevent/mitigate the risk.
12. Opportunity for improvement:
List out the improvements that have already been carried out.
Also list out the improvements to be carried out in the next period.
13. Cost of poor quality (COPQ):
Review the cost of poor quality data of the last 6 months against the target decided. Take action if it is found less than the target in any month. The cost of poor quality should be as minimal as possible.
14. Process effectiveness:
Overall equipment effectiveness OEE
15. Process efficiency:
Process efficiency refers to the extent to which a process or system can achieve its intended goals or objectives in a timely and cost-effective manner. It is a measure of how well a process or system is performing in terms of output and resource utilization.
Process efficiency can be evaluated by measuring the time, resources, and costs required to complete a process or achieve a desired outcome. A highly efficient process minimizes waste, reduces costs, and maximizes productivity while delivering high-quality results.
Improving process efficiency involves identifying areas of inefficiency and implementing measures to streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, and optimize resource utilization. This can involve automation, redesigning workflows, improving communication and collaboration, and leveraging technology to streamline and optimize processes. By improving process efficiency, organizations can reduce costs, improve productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction.
16. Product conformance:
Product conformance refers to the extent to which a product or service meets specified requirements, standards, and expectations. It refers to the product’s ability to function as intended and meet the needs of its intended users, while also complying with applicable regulations and industry standards.
Product conformance can be evaluated through various methods, including testing, inspection, and certification. Organizations may establish their internal standards or follow external standards set by regulatory bodies or industry associations. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and can enhance the credibility and marketability of the product.
17. Feasibility study during NPD and ECN:
Review the new product development status against the inquiry received. Also review that the feasibility should be done within 10 days.
18. Performance review of maintenance objective:
Review the maintenance objective against the target. e.g. Breakdown hours, Preventive maintenance as per Plan, OEE, MTTR and MTBF.
19. Warranty performance:
Review the status if you have any parts under warranty. If no such part exists, then it is OK.
21. Customer scorecards review:
Review the scorecard of all customers of the last 6 months. Also review the action taken when the score was lower.
22. Identification of potential field failure identified through risk analysis ( FMEA):
The potential field failures have been addressed in the process FMEA and the corresponding points are included in the control plan for implementation.
23. Actual field failures and their impact on safety or the environment:
The actual field failures have been addressed in the process FMEA and the corresponding points are included in the control plan for implementation.
24. Customer-Specific Requirements:
Customer-specific requirements or any other system-related requirements have to be taken into our QMS. All customer-specific requirements are considered. We should prepare a matrix for all customer & their requirements.
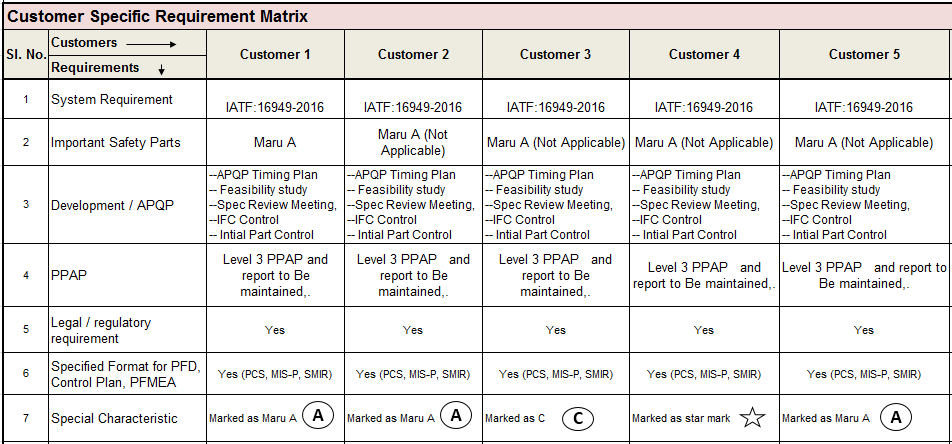
25. Kaizens:
Review the status of Kaizen done each month against the target. Also motivate employees to do the kaizens.
26. Business Plan:
A business plan is prepared and the same is available. This has been integrated with the QMS.
Action: The practice of integrating the business plan with the QMS is to be continued. Also monitoring of the improvement in business results by the implementation of QMS to be done.

